
The available data types in Tableau include text, date values, date & time values, numerical values, boolean values, geographical values, and cluster groups
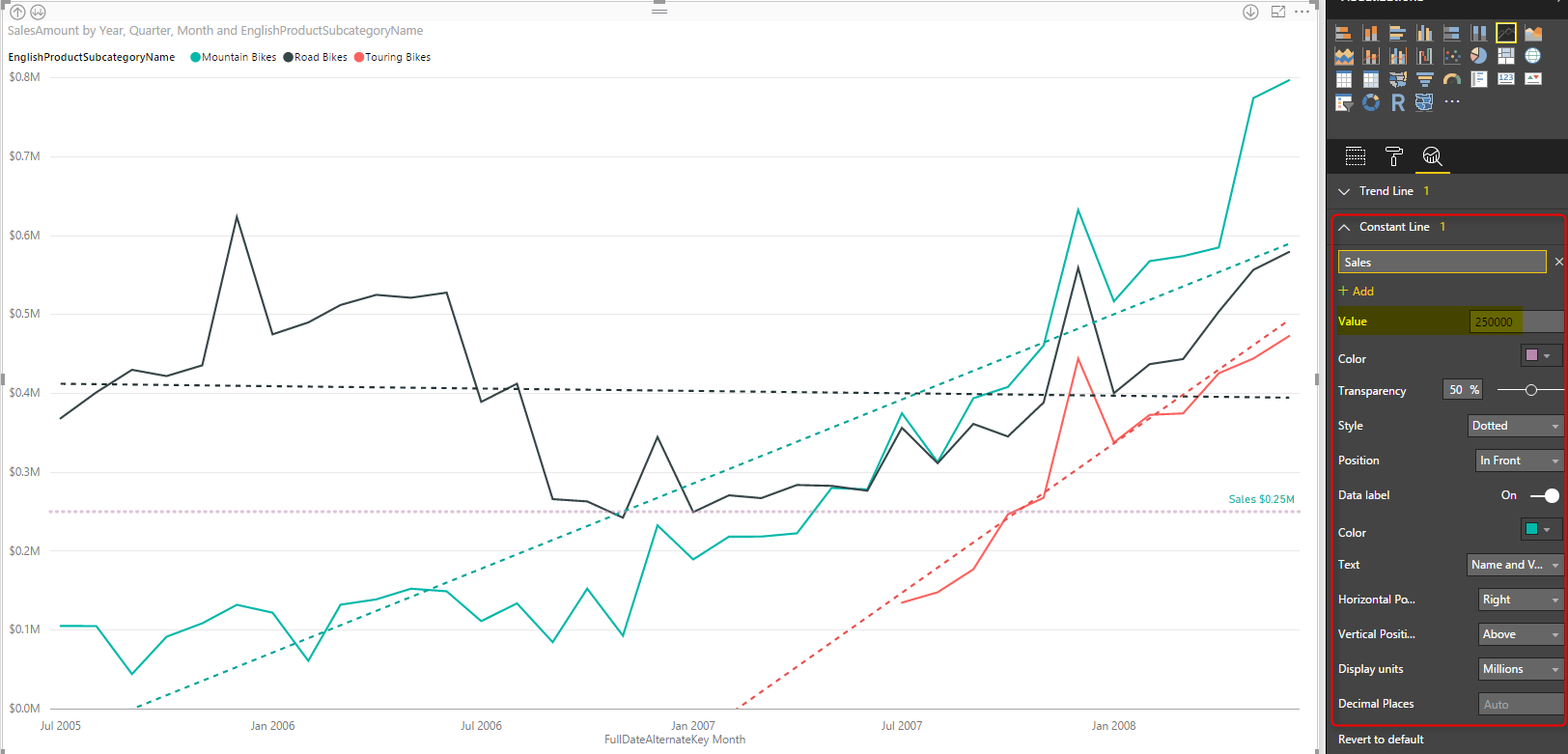
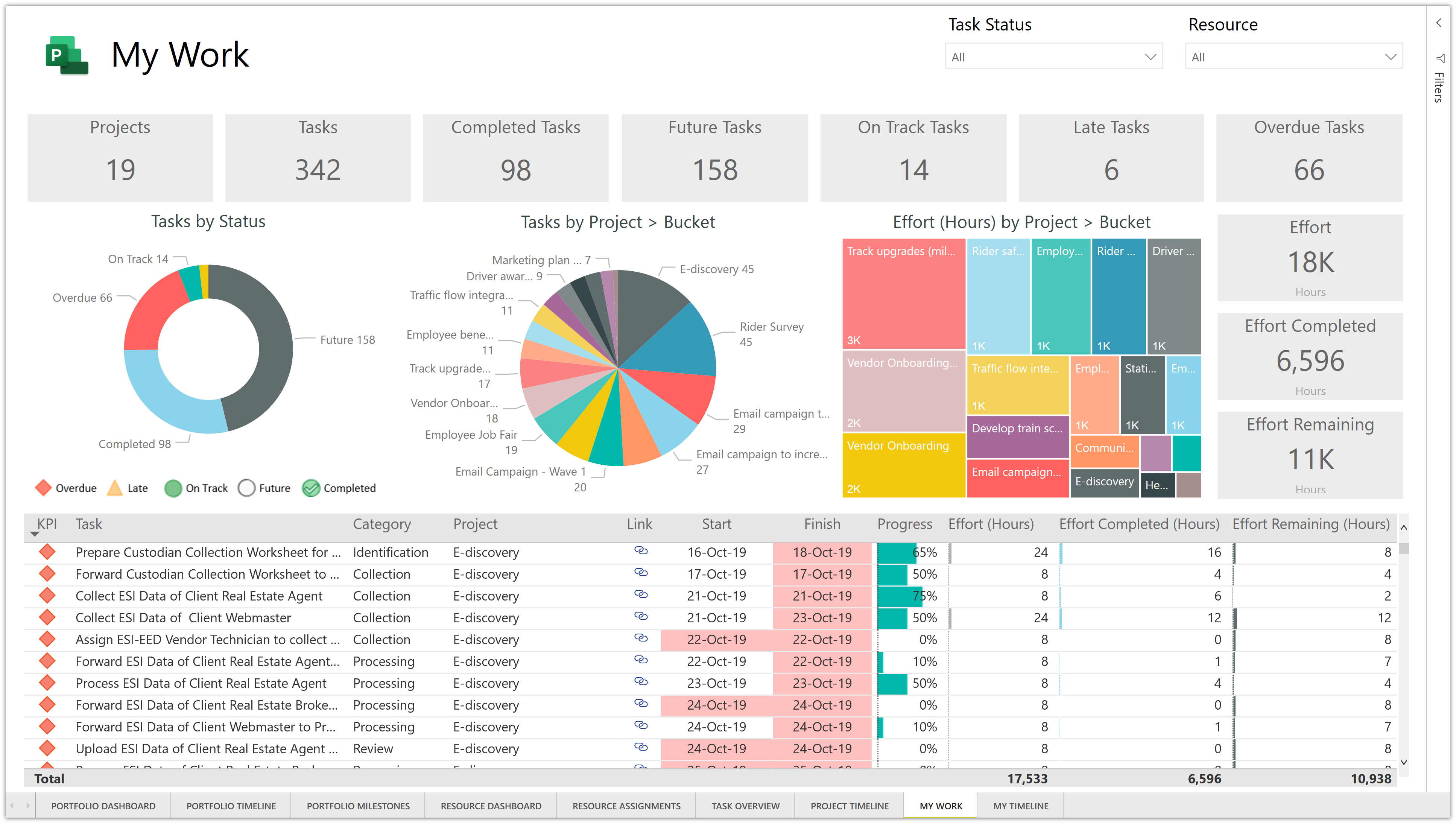
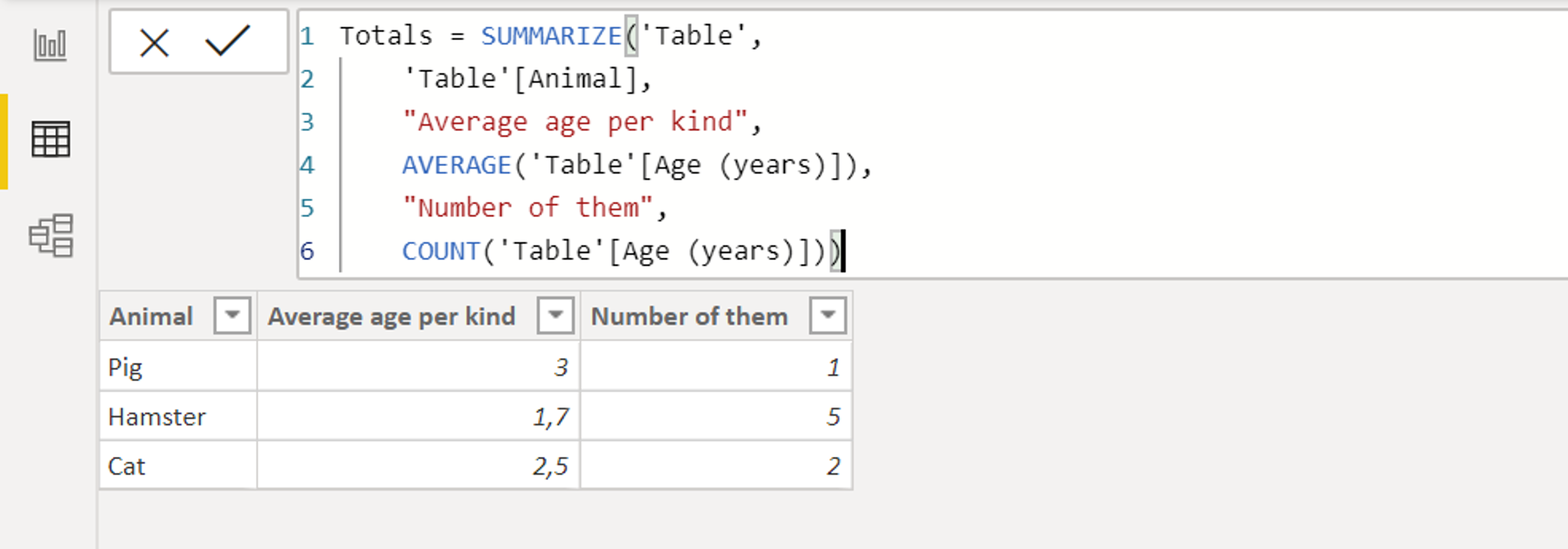
Data types: Every field has a data type which is determined by the type of information it contains.When dragged into a view, this data is aggregated, which is determined by the dimensions in the view Measures: A measure is a type of field that contains quantitative values (e.g.Dimensions dictate the amount of granularity in visualizations and help reveal nuanced details in the data Dimensions: A dimension is a type of field that contains qualitative values (e.g.They show up in the data pane and can either be dimension or measure fields Fields: Fields are all of the different columns or values in a data source or that are calculated in the workbook.When working with data in Tableau, there are multiple definitions to be mindful of Analytics: The analytics pane on the left-hand side lets you add useful insights like trend lines, error bars, and other useful summaries to visualizations.Data: The data pane on the left-hand side contains all of the fields in the currently selected data source.In the sidebar, you’ll find useful panes for working with data Story: A story is a collection of multiple dashboards and/or sheets that describe a data story.Dashboard: A collection of multiple worksheets used to display multiple views simultaneously.You can add shelves, cards, legends, visualizations, and more to a worksheet Worksheet: A worksheet is a single view in a workbook.A sheet can be any of the following and can be accessed on the bottom left of a workbook. Similar to Microsoft Excel, a Workbook can contain multiple sheets. Workbooks contain sheets, dashboards, and stories.
When working with Tableau, you will work with Workbooks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
